 The cooling system is to ensure the proper operating temperature of the engine. It includes a cooler, thermostat, flexible hoses and a network of channels in the block and engine head with precisely selected cross-sections, in which the coolant flows. This creates a protective coat, which collects the heat of combustion and conducts hot liquid through the pipes and channels to the radiator. The coolant circuit depends on the engine temperature.
The cooling system is to ensure the proper operating temperature of the engine. It includes a cooler, thermostat, flexible hoses and a network of channels in the block and engine head with precisely selected cross-sections, in which the coolant flows. This creates a protective coat, which collects the heat of combustion and conducts hot liquid through the pipes and channels to the radiator. The coolant circuit depends on the engine temperature.
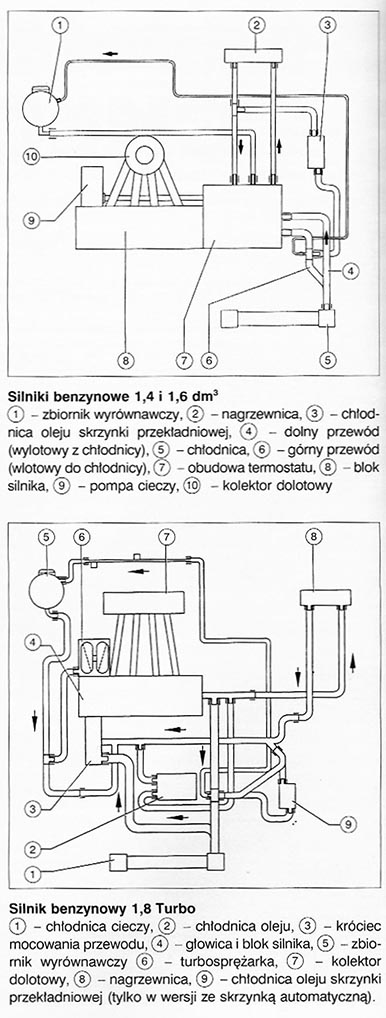
Coolant circuit
After starting a cold engine, the coolant circulates in a small circuit, covering only the engine and heating. In this circuit, the path to the radiator is blocked by a thermostat. The coolant returns directly to the engine and heats up quickly, which in turn allows you to quickly reach the correct operating temperature of the engine. Only after the liquid has reached a certain temperature, a cooler is turned on in the circuit. The thermostat opens the way to it and the cold liquid remaining in the radiator mixes with the already hot liquid from the short circuit. The mixing of the liquid is necessary to avoid the so-called. thermal shock of the engine.
With increasing coolant temperature, The thermostat opens the way to the radiator more and more and at the same time closes the shorter cycle. When the engine operating temperature is reached, liquid flowing from the bottom, cold exhaust line in the radiator enters the pump, which presses it to the engine block and cylinder head. From there, most of the liquid is routed through an open thermostat to the radiator, and the rest to the heat exchanger (heater) heating system. The cold liquid flowing out of the cooler makes room for the hot liquid, which is cooling down, flowing through the radiator fins, while driving, the engine temperature drops below a certain value, the thermostat shuts off the flow of coolant to the radiator pending, until the engine reaches the required operating temperature.
attention: Coolant circuit, thus, the routing of the lines in the cooling system is adapted to the particular engine. The figures below show simplified examples of solutions in the most popular engines.
Fluid pressure and fan
At normal engine operating temperature, there is an overpressure in the cooling system from 0,14 do 0.16 MPa. As a result, and due to various additives to the coolant, its boiling point is raised from 100 ° C to about 120 ° C. Higher engine operating temperature means more economic operation and fuel savings. When the pressure in the cooling system exceeds when the engine is hot 0,15 MPa, then the pressure valve on the expansion tank opens, through which a little vapor of the cooling liquid flows out. Despite this, the cooling system may overheat when driving around town. This is prevented by additional cooling of the radiator by means of a fan (one or more), which is controlled by a two-stage thermal switch. It is mounted on the left side of the radiator casing. At a coolant temperature of 92…97° C the first stage is turned on (half the speed). At a temperature of 99…105° C the thermal switch switches the second stage on (full fan speed). The fan is turned on periodically and the coolant circuit controlled by the thermostat allows the engine to work at the correct operating temperature, thus saving fuel.
Cooling liquid
The coolant is a mixture of water and anti-corrosion and anti-freeze agents. The anti-corrosion additive prevents scale build-up in the cooling system and the formation of rust spots. This additive loses its properties after approximately four years and the coolant must be replaced after this period. Volkswagen does not order the fluid to be changed regularly. Depending on the antifreeze used, the proportion of water in the coolant is up to 60%. These proportions should not be different also in summer.
All engines use a new reddish water and red G12 coolant, prepared according to the TL VW factory standard 774 D. This liquid must not be mixed with the previously used G agent 011 A8 C to protect against corrosion and freezing of liquids, as this can seriously damage the engine. The change in color of the liquid to brown is indicative of this, however, there was a mixture of the two types of protective measures. In this case, completely drain the cooling system, rinse it with water (run the engine for two minutes) and fill with new liquid.
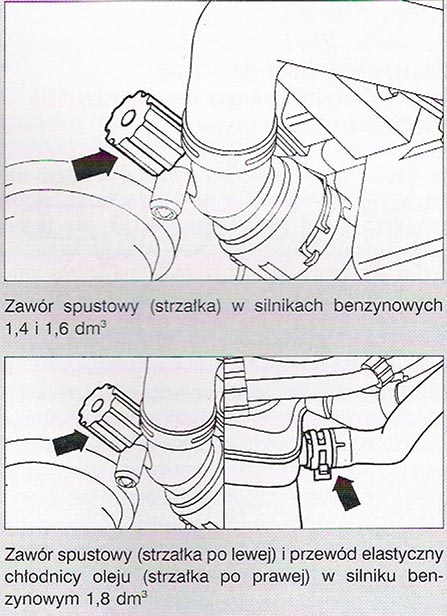

 Elements of the cooling system:
Elements of the cooling system: Checking the tightness of the cooling system:
Checking the tightness of the cooling system: The cooling system is to ensure the proper operating temperature of the engine. It includes a cooler, thermostat, flexible hoses and a network of channels in the block and engine head with precisely selected cross-sections, in which the coolant flows. This creates a protective coat, which collects the heat of combustion and conducts hot liquid through the pipes and channels to the radiator. The coolant circuit depends on the engine temperature.
The cooling system is to ensure the proper operating temperature of the engine. It includes a cooler, thermostat, flexible hoses and a network of channels in the block and engine head with precisely selected cross-sections, in which the coolant flows. This creates a protective coat, which collects the heat of combustion and conducts hot liquid through the pipes and channels to the radiator. The coolant circuit depends on the engine temperature.